PhishStrike Write-up
الحمد لله والصلاة والسلام على رسول الله وعلى آله وصحبه أما بعد:
Scenario:
As a cybersecurity analyst for an educational institution, you receive an alert about a phishing email targeting faculty members. The email, appearing from a trusted contact, claims a $625,000 purchase and provides a link to download an invoice.
Your task is to investigate the email using Threat Intel tools. Analyze the email headers and inspect the link for malicious content. Identify any Indicators of Compromise (IOCs) and document your findings to prevent potential fraud and educate faculty on phishing recognition.
Tools:
Email Header Analyzer
URLHaus
VirusTotal
MalwareBazaar
Link: https://cyberdefenders.org/blueteam-ctf challenges/phishstrike/
Writeup In Medium: https://medium.com/@GLITCHGC/phishstrike-write-up-767d44fe3e97
Okay Let’s Move on!

Questions:
1. Identifying the sender’s IP address with specific SPF and DKIM values helps trace the source of the phishing email. What is the sender’s IP address that has an SPF value of softfail and a DKIM value of fail ?

In this i used phishtool.com site

Go to Security Tap and you will find it (The answer will be highlight)
Answer: 18.208.22.104
2. Understanding the return path of the email helps in tracing its origin. What is the return path specified in this email ?

Answer: erikajohana.lopez@uptc.edu.co
3. Identifying the source of malware is critical for effective threat mitigation and response. What is the IP address hosting the malicious file associated with malware distribution ?

Answer: 107.175.247.199
4. Identifying malware that exploits system resources for cryptocurrency mining is critical for prioritizing threat mitigation efforts. The malicious URL can deliver several malware types. Which malware family is responsible for cryptocurrency mining ?

Can you use urlhaus.abuse.ch to check
Answer: CoinMiner
5. Identifying the specific URLs malware requests is key to disrupting its communication channels and reducing its impact. Based on the previous analysis of the cryptocurrency malware sample, what does this malware request the URL?

Ok after a little research, from urlhaus.abuse.ch I got the sha256 hash for the malware 453fb1c4b3b48361fa8a67dcedf1eaec39449cb5a146a7770c63d1dc0d7562f0

And put it in Virustotal and look for Relations tap and i get it
6. Understanding the registry entries added to the auto-run key by malware is crucial for identifying its persistence mechanisms. Based on the BitRAT malware sample analysis, what is the executable’s name in the first value added to the registry auto-run key ?

This one choose BitRat Signature and copy the SHA256

go to bazaar.abuse.ch and search for sha256:bf7628695c2df7a3020034a065397592a1f8850e59f9a448b555bc1c8c639539

scroll down to get the ANY.RUN report

Simple analysis and you will find it
Answer: Jzwvix.exe
7. Analyzing the HTTP requests made by malware helps in identifying its communication patterns. What is the HTTP request used by the loader to retrieve the BitRAT malware ?

will find it in HTTP Requests Tap
8. Identifying the SHA-256 hash of files downloaded by a malicious URL aids in tracking and analyzing malware activities. According to the BitRAT analysis, what is the SHA-256 hash of the second file downloaded and added to autorun keys ?

We know that the first was Jzwvix.exe. To know the second, you can check the processes as in the previous image
Answer:bf7628695c2df7a3020034a065397592a1f8850e59f9a448b555bc1c8c639539
9. Introducing a delay in malware execution can help evade detection mechanisms. What is the delay (in seconds) caused by the PowerShell command according to the BitRAT analysis ?

copy this base64 code and let’s decoded
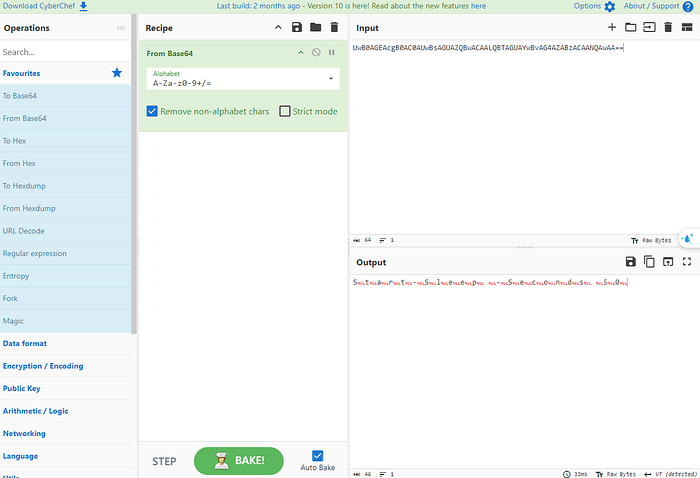
I use cyberChef for this and as you see output is “start sleep seconds 50”
Answer: 50
10. Tracking the command and control (C2) domains used by malware is essential for detecting and blocking malicious activities. What is the C2 domain used by the BitRAT malware ?

check DNS Requests Tap to find the answer
Answer: gh9st.mywire.org
11. Understanding the methods malware uses for exfiltrating data is crucial for detecting and preventing data breaches. According to the AsyncRAT analysis, what is the Telegram Bot ID used by the malware to exfiltrate stolen data ?

Back to https://urlhaus.abuse.ch/url/2381718/ but this time will choose AsyncRAT, after search in the previous site i don’t find anything, So I decided to use another platform like tria.ge

go to the report in tria.ge, and scroll down to get Network section and as you see in previous image the malware use BOTID to exfiltrate stolen data
Answer: bot5610920260
Last updated